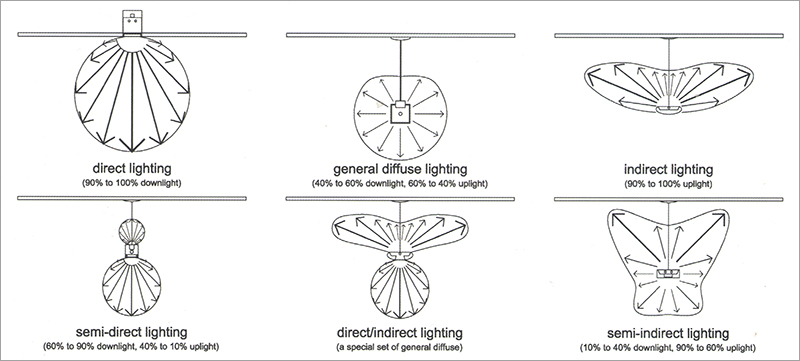
Direct lighting luminaires distribute 90 to 100 percent of the emitted light in the general direction of the surface to be illuminated. The term generally refers to light emitted in a downward direction. Troffers and downlights are two types of direct lighting luminaires.
Semi-direct lighting luminaires distribute 60 to 90 percent of the emitted light downward and the balance upward. The shadows generated by semi-direct lighting are diffused and do not cause discomfort. Semi-direct lighting is employed in applications where strong light is not necessary e.g., stairways, corridors, and storage areas.
General diffuse lighting luminaires distribute 40 to 60 percent of the emitted light downward and the balance upward, in some cases with a strong component at 90 degrees (horizontal). This type of light distribution integrates the characteristics of direct lighting and those of indirect lighting.
Direct-indirect lighting is a variant of general diffuse lighting in which the luminaires give off little or no light at angles near the horizontal. Because this characteristic result in lower luminances in the direct glaze zone, direct-indirect luminaires are generally more desirable than general-diffuse luminaires that distribute the light about equally in all directions.
Semi-indirect lighting luminaires distribute 60 to 90 percent of the emitted light upward and the balance downward, similar to those of indirect lighting systems with the exception that the downward component usually creates a luminaire luminance that closely matches that of the ceiling. Semi-indirect lighting scheme is primarily used for indoor light decoration purposes.
Indirect lighting luminaires distribute 90 to 100 percent of the emitted light upward. In a well-designed installation, the entire ceiling becomes the primary source of illumination, and shadows will be virtually eliminated. In this lighting scheme more than 90% of total luminous flux is thrown upwards to the ceiling for diffuse reflection by using inverted or bowl reflectors. Since the indirect lighting the ceiling and upper walls must reflect light to the work plane, it is essential that these surfaces have high reflectances.












